Vocabulary:
- Consumer – an organism that eats other organisms (plants and / or animals) for food
- Decomposer – an organism that gets energy by feeding on dead materials and waste
- Dependent – to rely on someone or something else
- Ecosystem – the living and nonliving components of an area
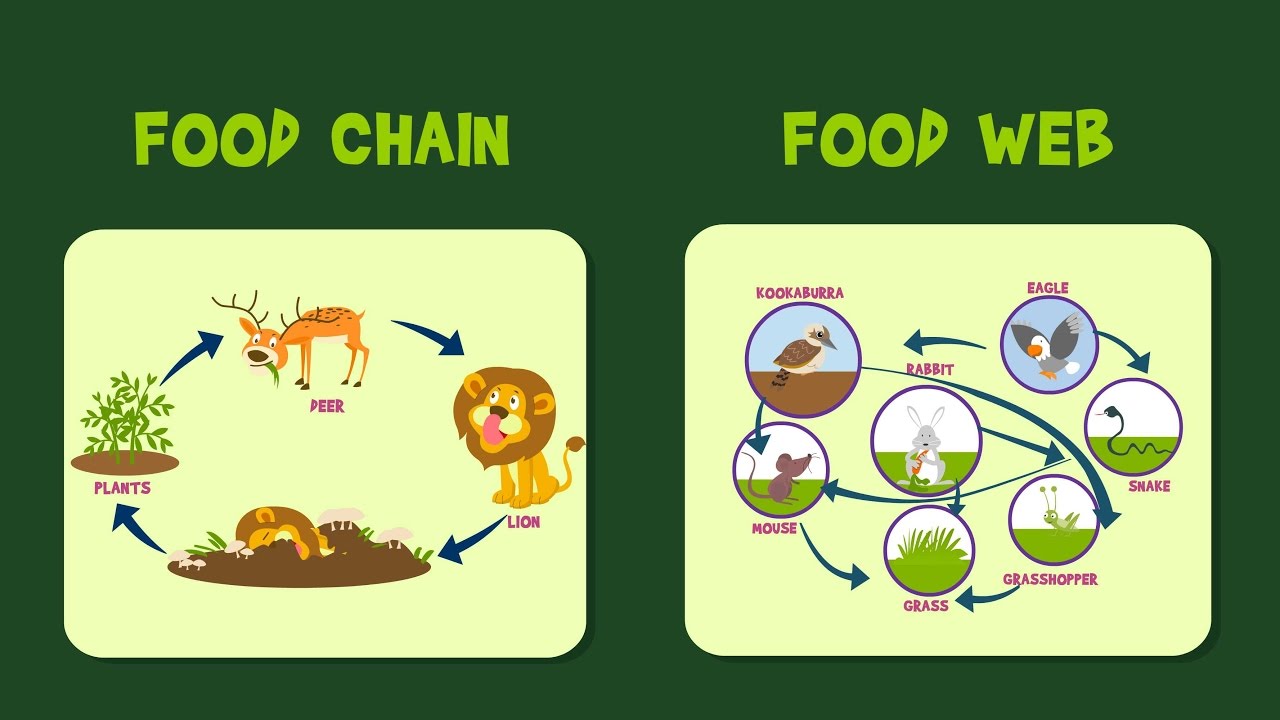
- Food chain – a representation of the flow of energy from the Sun through producers to consumers and decomposers in an ecosystem
- Food web – a representation of several overlapping food chains in an ecosystem; includes the flow of energy from the Sun through producers to consumers and decomposers through multiple pathways
- Habitat – the place where an organism lives; habitats supply the organism with food, shelter, moisture, and temperature for survival
- Model – a picture, an idea, or an object that represents an object, a system, or a process and is used to help with understanding; models have advantages and limitations
- Producer – an organism that makes its own food (e.g., plants)
NEEDS OF PRODUCERS AND CONSUMERS TO MAKE / OBTAIN FOOD
- Producers (plants) use the following to make their own food:
- Sunlight (energy)
- Water
- Carbon dioxide (gas in the air)
- Plants take in carbon dioxide and give off oxygen
- Consumers’ (animals) dependence on other organisms for food
- Animals eat animals and / or plants
- Herbivores – animals that feed only on producers (plants)
- Carnivores – animals that feed only on other animals
- Omnivores – animals that feed on plants or other animals
- Predator / prey relationships
- Animals eat animals and / or plants
FLOW OF ENERGY THROUGH FOOD WEBS
- Food web – a representation of several overlapping food chains in an ecosystem; includes the flow of energy from the Sun through producers to consumers and decomposers through multiple pathways
- Producer – an organism that makes its own food (e.g., plants)
- Consumer – an organism that eats other organisms (plants and / or animals) for food
- Decomposer – an organism that gets energy by feeding on dead materials and waste
- Flow of energy (beginning with the Sun)